In computer science there are many different types of data structures to help us store and organize information. Two common data structures are stacks and queues. Stacks and queues are simple data structures.
Let’s talk about Stacks
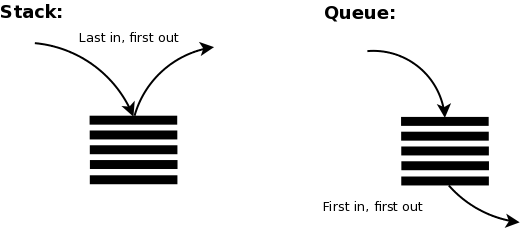
Stacks are called LIFO (last in, first out). Think of stacks like a stack of plates. In order to reteive data you, you have to pull from the top. With a stack of places you can’t just pull a plate out from the middle of a stack of plates, you have to pick up the top one. A stack data structure is the same. You have to take each element from the top.
A stack is an object that holds data. Within the stack you have to have a storage variable which can be an array or an object. Stacks are used because they take up less space in memory. They are also good to use because, at least for retrieving and adding data and a 0(1), or constant time complexity. An example of when we might use a stack is like the back button on our browswer. If you are on a website, let’s say Facebook, but then you go to Twitter, then you go to Gmail. If you hit your back button, it will take you from Gmail, to Twitter, not Facebook. The back button will take you to the last page you visited. Last in, first out.
Stacks have several methods that can be used to access and change data within the stack. Some of those methods are:
- Push (adds data to the stack)
- pop (removes data from the stack)
- peek (lets you see the last element in the stack)
- size (tells you the size of the stack)
Queueueueueueueueus
Queues can be looked at like a line of people. Queues are FIFO (first in, first out). Much like people who get in a line for something, such as going into a movie theater, generally the first person who gets in the line will be the first people who gets to enter the movie theater. Queues are the same way. The first bit of data entered will be the first one accessed.
Queues are also objects that hold a storage variable that can either be an array or object. Queues also have a 0(1), or constant time complexity, when retrieving or adding data. An example of something that might use a queue is an event handler. If you have a website that has several different interactive parts, such as clicking different spots, or entering texts, the site could use a queue to handle each event, one at a time, in the order in which they were triggered. If you type something in a box with a submit button, and then click on a button that maybe takes you to another page, the site will process the click on the submit button first, then it will take you to the other page.
Queues also have methods that can be used to manipulate data:
- enqueue (adds values to queue)
- dequeue (removes a value from queue)
- size (gives the size of the queue)
- contains (used to see if a value exists in the queue)